HS-LS1-5. Use a model to illustrate how photosynthesis transforms light energy into stored chemical energy.
Photosynthesis is a crucial process used by plants and other photosynthesizing organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy. This process is essential for life on Earth as it provides the primary source of energy for almost all living organisms. In this review, we will explore how photosynthesis transforms light energy into stored chemical energy, focusing on the inputs and outputs involved, as well as the energy transformations that occur.
Main Concepts
Photosynthesis: Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, algae, and some bacteria use light energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. This process takes place mainly in the chloroplasts of plant cells.
Inputs and Outputs: The main inputs for photosynthesis are light energy, carbon dioxide (CO2), and water (H2O). The outputs are glucose (C6H12O6) and oxygen (O2).
Energy Transformation: In photosynthesis, light energy is captured by chlorophyll and other pigments in the chloroplasts. This energy is then used to drive chemical reactions that transform carbon dioxide and water into glucose. The energy stored in glucose can be used by the plant for growth, reproduction, and other processes.
Photosynthesis Equation: The general chemical equation for photosynthesis is:
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energyThis equation summarizes the transformation of light energy into chemical energy stored in glucose, with oxygen being released as a byproduct.
NGSS Aligned Testing Question
Coral reefs form over many thousands of years as tiny animals called polyps produce a calcium carbonate (CaCO ) 3 skeleton. This rock-like skeletal structure adds new layers over time, forming the three-dimensional habitat that makes up the reef. Most polyps depend on a beneficial relationship with a diverse group of photosynthetic algae called zooxanthellae. When coral polyps are under stress, some of the zooxanthellae leave the coral polyps, resulting in bleaching. Without the zooxanthellae algae, the coral takes on a white appearance and will eventually die.
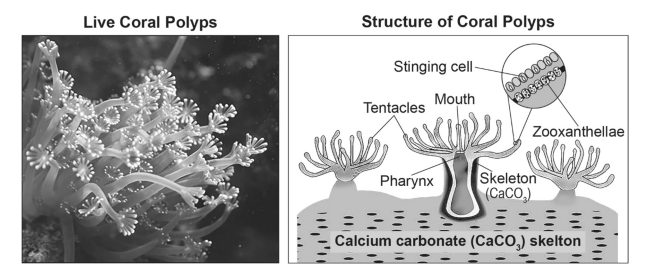
The illustration below provides an enlarged view of a single polyp tentacle that shows the relationship between the zooxanthellae and a healthy coral polyp.
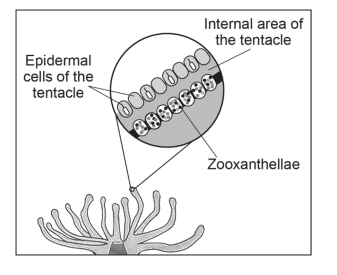
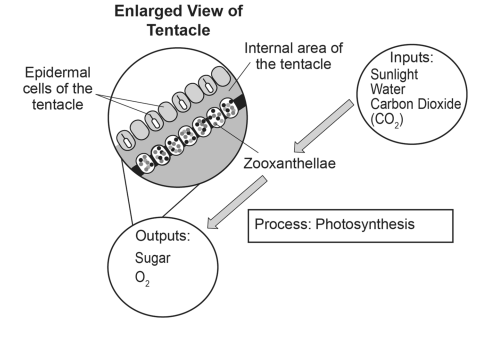
| Complete the model below to illustrate the process occurring in the zooxanthellae located in the cells of the coral polyp. Your model should include all inputs of both matter and energy and identify the process involved.
|
|
|---|---|
Review Questions and Answers
- What is photosynthesis?
- Where does photosynthesis occur in plant cells?
- What are the main inputs of photosynthesis?
- What are the main outputs of photosynthesis?
- How is light energy used in photosynthesis?
- What is the general equation for photosynthesis?
- What does glucose produced in photosynthesis provide for the plant?
- Why is oxygen a byproduct of photosynthesis?
- How can models help illustrate photosynthesis?
- What role do chlorophyll and other pigments play in photosynthesis?
- What is the importance of photosynthesis for life on Earth?
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria use light energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
Photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplasts of plant cells.
The main inputs are light energy, carbon dioxide (CO2), and water (H2O).
The main outputs are glucose (C6H12O6) and oxygen (O2).
Light energy is captured by chlorophyll and other pigments and used to drive the chemical reactions that convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose.
The general equation is: C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy.
Glucose provides the plant with stored chemical energy that can be used for growth, reproduction, and other vital processes.
Oxygen is a byproduct because it is released during the splitting of water molecules in the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis.
Models, such as diagrams, chemical equations, and conceptual models, can help illustrate how light energy is converted into chemical energy and how the inputs and outputs of photosynthesis are related.
Chlorophyll and other pigments capture light energy, which is then used to drive the chemical reactions of photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis is crucial because it provides the primary source of energy for nearly all living organisms and releases oxygen into the atmosphere, which is essential for the respiration of most life forms.
*continue your studies by accessing another review sheet below*
HS. Structure and Function: HS-LS1-1 : HS-LS1-2 : HS-LS1-3
HS. Matter and Energy in Organisms and Ecosystems: HS-LS1-5 : HS-LS1-6 : HS-LS1-7 : HS-LS2-3 : HS-LS2-4 : HS-LS2-5
HS. Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems: HS-LS2-1 : HS-LS2-2 : HS-LS2-6 : HS-LS2-7 : HS-LS2-8
HS. Inheritance and Variation of Traits: HS-LS1-4 : HS-LS3-1 : HS-LS3-2 : HS-LS3-3 : HS-LS1-8
HS. Natural Selection and Evolution: HS-LS4-1 : HS-LS4-2 : HS-LS4-3 : HS-LS4-4 : HS-LS4-5
Disclaimer: The information provided is intended to serve as a study guide based on a contextual analysis of the NGSS standards for the Life Science Biology assessment. These study guides should be used as a supplement to your overall study strategy, and their alignment to the actual test format is not guaranteed. We recommend that you consult with your instructor for additional guidance on exam preparation.